What is an endoscopy?
 A small light and camera on the end called an endoscope, a device with the help of the esophagus,
A small light and camera on the end called an endoscope, a device with the help of the esophagus,
stomach, duodenum, and colon endoscopy is to examine the gastrointestinal tract covering that allows processing. It is a very reliable and effective method of revealing the factor that causes digestive system disorders. It can be used in the diagnosis of the disease, as well as for the treatment of gastric bleeding and removal of polyps in the stomach, it is widely used. If any tumor formation is observed during the procedure, a biopsy can be taken to make a definitive diagnosis and to investigate the presence of a bacterium called Helicobacter Pylori in the stomach. Endoscopy is divided into two, namely gastroscopy and colonoscopy. In the gastroscopy procedure, the stomach and part of the duodenum are evaluated; in the colonoscopy, the condition of the large intestine is evaluated.
Who is endoscopy applied to?
* Those who complain of stomach pain and anemia problems
* Those who have complaints such as difficulty swallowing, heartburn, reflux, burning in the chest and persistent nausea vomiting, fever and weakness
• Under the control of those who experience weight loss of unknown cause, patients undergoing gastric surgery, and patients who have previously undergone endoscopy and been given medication
* Those who have brown vomiting, red blood coming from the mouth, or black defecation
• To place a gastric catheter in patients who have to be fed by inserting a hose into the stomach
* Patients who suffer from constipation for a long time and do not respond to treatment with medication
* For those who have bleeding in the breech, ulcerative colitis and Chron patients
* In the detection of abnormalities in the intestinal wall, polyps, diverticula, tumors and vascular pathologies
• When suspicious lesions are seen as a result of examinations such as tomography and medicated bowel and stomach film, an endoscopy procedure is performed to remove parts from these lesions.
How is endoscopy performed?
The endoscopy procedure, which is performed with the help of a bendable pipe 8-10 millimeters thick, which has its own camera and a special light source, allows imaging of the organs of the digestive system. The images taken with the help of the camera on the tube are projected onto the screen, and the doctor evaluates the internal surface of the organs by looking at these images. During the procedure, the patient's oxygen level and your condition are monitored. When the doctor deems it necessary, he can take parts to get a definitive diagnosis of the disease. In addition, if there is bleeding, it can stop bleeding or remove polyps. The gastroscopy procedure, in which the organs of the upper digestive system are visualized, takes about 3-5 minutes, and the colonoscopy procedure, in which the large intestine is visualized, takes about 15-20 minutes. For the gastroscopy procedure, the patient should not eat anything for at least 6 hours before the procedure, and for the colonoscopy procedure, bowel cleansing with special medications should be performed at least 2 days before. For endoscopy, which is a painless and painless procedure, if there is no special reason affecting the patient's general health, relaxing and light sleeping medications are given through the arm vein as a preliminary preparation.
There are usually no problems after the endoscopy procedure, but some patients may experience a sore throat for a few days. Slight drowsiness or fatigue may be observed due to the sedative medications given. However, if there are conditions such as abdominal pain, vomiting, blood coming from the mouth, fever and difficulty breathing that become increasingly severe in the 48-hour period following the procedure, a doctor should be visited without wasting time.
Other Pages
- Wounds after surgery
- Will there be any scars in breast reduction surgery?
- Will Porcelain Veneer Change Color in the Future?
- Why does the vagina smell?
- Why Does the Sound Come From The Knees?
- Why Does Sensitivity Occur in Teeth?
- Why Does Ear Pain Occur?
- Why Does cherry angioma Come Out?
- Why do we become food addicts?
- Why do gallstones form
- Why do babies have neck curvatures?
- Why do babies cry?
- Who can't donate their kidneys?
- Which Vacuum Oil Extraction Opera is Remembered?
- WHICH PROTECTION METHODS CAN BE PREFERRED AFTER BIRTH?
- WHICH PROTECTION METHODS CAN BE PREFERRED AFTER BIRTH?
- Which is the Best Hair Transplant Method?
- Which glasses should be preferred in summer
- When Will I Notice the Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Treatment and How Long Does It Take?
- When Should I Get an Allergy Test?
- When and How is Immunotherapy Administered?
- What You Need to Know About Buckthorn Oil
- What we need to know about minerals
- What triggers hoarseness?
- What to Eat For Biotin Deficiency?
- What tests determine the source of impotence?
- What should we do for a healthy skin
- What Should We Avoid After Bleaching?
- What should kidney stone patients pay attention to?
- What should kidney stone patients pay attention to?
- What should I eat at Iftar, what should I avoid?
- What should be the amount of urea in the blood?
- What should be the amount of urea in the blood?
- What Should Be Done to Have Healthy Gums?
- What Should Be Done Against Night Plaque
- What should be considered in order to prevent lumbar hernia
- What Should be Considered Before and After Tummy Tuck Surgery?
- What Should Be Considered After Breast Reduction Surgery?
- What is Zinc Deficiency?
- What is Yellow Spot Disease?
- WHAT IS WAIST COLD?
- What is vergito ?
- What is Vascular Occlusion
- What is varicose veins treatment?
- What is Ulthera?
- What is Tummy Tuck Aesthetics?
- What is Tummy Tuck Aesthetics?
- What is tuberculosis ?
- What is trypophobia?
- What is trigger finger?
- What Is the Use of Thyme Tea?
- What is the PSA test?
- What is the PSA test?
- WHAT IS THE PROBLEM OF URINE INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN?
- WHAT IS THE PROBLEM OF URINE INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN?
- What is the Morning-After Pill?
- What is the HPV virus?
- What is the hormone progesterone?
- What is the Heimlich Maneuver?
- What is the Flu Vaccine?
- What is the Effect of Vitamin A on the Eyes ?
- What is the Effect of Excessive Alcohol Consumption on the Body?
- What is the definition of a stroke?
- What is the curvature of the nose (Septum Deviation)
- What is the Cuban cancer vaccine? To whom can it be applied?
- What is the biological clock setting
- What is the Best Time for Circumcision?
- What is the BA2 variant
- What is the Age of Scone Ear Surgery (Otoplasty)?
- What is Tea Tree Oil?
- What is Sunstroke?
- What is Sugar Loading in Pregnancy?
- What is St. John's Wort Oil?
- What is sputum?
- What is spring allergy?
- What is Splint? In what cases is it applied?
- What is social phobia?
- What is Social Intelligence?
- What is Snoring?
- What is snoring?
- What is Silicosis?
- What is sickle cell anemia ?
- What is SIBO?
- What is Shoulder Impingement Syndrome?
- What is serotonin syndrome?
- What is sepsis?
- What is sedation
- What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
- What is sciatica?
- WHAT IS RINGWORM?
- What is rheumatism?
- What is Reflux?
- What is rambutan fruit?
- What Is Radish Good For?
- What is PRP?
- What is PRP treatment?
- What is prostate cancer?
- What is prostate cancer?
- What is prolotherapy?
- What is Priapism?
- What is postural disorder
- What is Porcelain Filling?
- What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
- WHAT IS PİTUİTARY ADENOMAS
- What is Physical Therapy?
- What is Phenylketonuria?
- What is Permeable Bowel Syndrome?
- What is Periodontal Inflammation Treatment?
- What is pelvic organ prolapse
- What is PCR Test?
- What is Panic Attack?
- What is painless bloody urine
- What is Ozone Therapy?
- What is Otosclerosis Disease?
- What is otitis media?
- What is Othello Syndrome?
- What is Osteopathy?
- What is nymphomania?
- What is Norovirus?
- What is Myasthenia Gravis?
- What is Ms ?
- What is Migraine, What are its Types?
- What Is Melon Good For?
- What is meditation?
- What is Lupus?
- What is leukemia
- What is Lazy Eye ?
- What is Laser Lipolysis?
- What is laparoscopy ?
- What is kyphosis?
- What is kidney inflammation?
- What is keratoconus?
- What is kefir?
- What is Kawasaki Disease?
- What is Jaw Bone Melting?
- What is itching in the body?
- What is itching during pregnancy
- What is iron deficiency?
- What is ingrown hair (Pilonidal Sinus)?
- WHAT IS INGENIC HERNIA?
- What is Individual Therapy?
- What is impotence?
- What is immunotherapy
- What is hypothyroidism?
- What is herpes?
- What is hepatitis b?
- What is Hemorrhoids (Hemorrhoids)?
- What is Hemorrhoids (Hemorrhoidal Disease)?
- What is Hemiplegia?
- What is heart rate?
- What is Heart Palpitations (Arrhythmia)?
- What is heart failure?
- What Is Good for a Burn Scar?
- What is genital wart ?
- What Is Foot Odor?
- What is food poisoning
- What is Food Addiction?
- What is fluorosis?
- What is Fibromyalgia ?
- What is fever ?
- What is eye redness?
- What is Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism)? Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
- WHAT IS ESOPHAGEN CANCER?
- What is Escape Disease?
- What is endoscopy?
- What is endometriosis (chocolate cyst)?
- What is elephantiasis (lymphedema)?
- What is earwax?
- What is earthquake phobia
- What is ear congestion?
- What is Dyspepsia?
- What Is Dry Eye Syndrome?
- What is drug addiction?
- What is Down Syndrome?
- What is diabetes?
- What is Dermapen?
- What is depression? / how to get rid of it?
- What is dementia?
- what is cystis ?
- what is cystis
- What is croup disease ?
- What is cortisone?
- What is Coronary Bypass Surgery?
- What is COPD?
- What is Constipation?
- What is conjunctivitis in winter?
- What is chronic fatigue syndrome?
- What is caffeine?
- What is butterfly disease (Lupus)?
- What is burnout syndrome?
- What is Bruxism (Tooth Clenching)?
- What is brucella?
- What is Breast Reduction Surgery?
- What is Botulinum Toxin?
- WHAT IS BONE INFLAMMATION?
- What Is Blood In The Urine?
- What is Bleeding Gums?
- What is Bladder Cancer?
- What is Black Fungus Disease?
- What is Appendicitis?
- What is Anthrax Disease?
- What is Anise?
- What is anesthesia ?
- What Is Anemia?
- What is anal fissure (anal fissure)?
- What is an undescended testicle
- What is an Umbilical Hernia?
- What is an endoscopy?
- What is an allergic catarrh
- What is ALS disease?
- What is allergic rhinitis in children
- What is Alcohol Dependence
- What is AIDS disease?
- What is Adrenal Gland Tumor (Peochromocytoma)?
- What is Adrenal Gland Tumor (Peochromocytoma)?
- What is adenoid?
- What is a Wart?
- What is a Uterine Film (HSG)?
- What is a tilt test?
- What is a Thyroid Nodule?
- What is a Smear Test?
- What is a Sebaceous Gland (Lipoma)? What Are The Causes?
- What is a premature baby ?
- What is a premature baby
- WHAT IS A POLYP IN THE BOTTOM?
- What Is a Mouth Wound?
- What is a Meniscus Tear?
- What is a Mediterranean diet (Mediterranean diet)?
- What is a hydrocele?
- What is a Hybrid Breast Augmentation Surgery?
- What is a Heart Hole?
- What is a Heart Attack?
- What is a head injury
- What is a Food Pyramid?
- What is a Flea Bite?
- What is a diet?
- What is a Bone Density Test?
- What is a black spot?
- What is a Birthmark?
- What is a biopsy?
- What exactly is Diarrhea?
- WHAT DOES ZINC DEFICIENCY LEAD TO?
- What does growth hormone deficiency lead to?
- What Causes Coughing in Children?
- What Causes Bradycardia?
- What Causes Blood to Come From the Urine (Hematuria)?
- What are the ways to sleep comfortably in summer
- What are the ways to reduce the risk of cancer
- What are the ways to prevent food poisoning in hot weather?
- What Are the Triggers for Chocolate Allergy?
- What Are the Triggers for Chocolate Allergy?
- What are the Treatment Methods of Polyps?
- What are the treatment and surgical methods of heart failure?
- What are the symptoms of vaginal discharge?
- What are the Symptoms of Hemorrhoids (Hemorrhoids)?
- What are the symptoms of fibromyalgia?
- What Are the Symptoms of Cholesterol?
- What Are the Symptoms of Cataracts? How Is It Treated?
- What are the Stages of Diabetic Foot?
- What are the Risks of Lumbar Hernia Surgery?
- What are the Risks of Breast Reduction Surgery?
- WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR WOMEN NOT TO URINATE ?
- WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR WOMEN NOT TO URINATE ?
- What Are the Nutritional Values of Watermelon?
- What are the methods to strengthen memory .
- What Are the Effects of the Flu Vaccine?
- WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF URINE INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN?
- WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF URINE INCONTINENCE IN CHILDREN?
- WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF URINE BLEEDING?
- WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF URINE BLEEDING?
- What are the Causes of Triggering of Skin Diseases in Diabetes?
- What Are the Causes of Light Flashing in the Eye?
- What are the causes of fatigue?
- What are the Causes of Congenital Heart Diseases?
- What are the Benefits of Walking?
- What are the benefits of figs?
- What Are the Benefits of Cinnamon?
- What are the benefits of breast milk?
- What Are the Benefits of Apple Cider Vinegar?
- What Are the Basic Requirements of the Family?
- What are Testicular Diseases?
- What are sexually transmitted diseases?
- What are ovarian cysts ?
- What are lens diseases ?
- What are Heart Valve Diseases?
- What are gallstones?
- What are foot insoles? How is it used?
- What are dental prostheses
- What are dental emergencies?
- Weight Loss After Tube Stomach Surgery
- Ways to Cope With Stress
- Vitamins and Minerals in Lettuce
- Vegetarian Nutrition
- Vegan Nutrition Types
- Unexplained bleeding in the joints can be a sign of hemophilia
- Unconscious use of painkillers
- Types of Klinefelter Syndrome
- Treatment options for gallstnes include:
- Treatment of small cell lung cancer
- Treatment of Sleep Apnea
- Treatment of lymphoma
- Treatment of lymphedema
- Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Treatment of diabetes
- Treatment methods of kidney failure
- To Whom Is Physical Therapy Applied?
- To whom can leaf porcelains be applied?
- To protect against varicose;
- Tips for ankle health
- THINGS TO DO AFTER BREAST AESTHETICS SURGERY
- Things to Consider While Going on a Long Journey
- Things to Consider After Making a Temporary Prosthesis Over the Implant
- The problem of not getting milk in mothers
- The problem Of A Large Forehead in Women?
- The most common complaints of patients with dry eyes are
- The importance of nutrition in depression
- The head of everything is the ”BRAIN"
- The Harms of Using Unnecessary Antibiotics?
- The benefits of Vitamin B12 and what to look for in its deficiency
- The benefits of melatonin hormone and what to do in case of its deficiency
- The Benefits of Hazelnuts
- The Benefits of Grape Molasses during Pregnancy
- The Benefits of Dark Chocolate
- The Benefits of persimmon
- Symptoms of lymph node inflammation
- Symptoms of Croup Disease
- Symptoms of Castleman's disease
- SYMPTOMS OF BONE INFLAMMATION
- Strengthen your immunity against spring fatigue
- Spring allergy medication reduces complaints
- So how do we get vitamin D?
- Skin spots caused by sun rays
- Sex life after kidney transplant
- Scoliosis Treatment in Children
- Safe Medication Use
- Risk Factors Triggering Heart Attack
- Regular sleep for strong immunity
- Recovery After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
- Recommendations for staying healthy during Ramadan
- Recommendations for Healthy Eating During Pregnancy
- Quitting Smoking and Controlling Weight Gain
- Protect your heart with these foods
- Prominent Ear Surgery
- Prohibitions After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
- PIEZO Rhinoplasty (ULTRASONIC RHINOPLASTY)
- Pica Syndrome: What is It and Why Does It Happen?
- Penis Enlargement And Thickening ?
- Osteoporosis (Bone Loss)
- NUTRITIONAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHEMOTHERAPY PATIENTS ?
- Nutrition During Pregnancy
- Nutrition During Menopause
- Nose Tip Aesthetics
- Neck Hernia
- Major Symptoms in Breast Cancer
- LYM (Lymphocyte) Height
- Liposuction Surgery
- Is There an Age Limit for Penis Surgery?
- Is There An Age Limit For Mammography?
- Is There an Age Limit for Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Aesthetics) ?
- Is There a Relationship Between Kidney Stones and Erection?
- Is Teeth Bleaching Harmful?
- Is pain-free life possible?
- Is not being able to get out of bed in the morning a sign of illness??
- Is It Possible to Smoke After Bleaching?
- Is it Possible To Avoid A Heart Attack?
- Is It Necessary to Renew the Brain Battery?
- Is it bad to eat the same things every day?
- Is Implant Harmful?
- is gas extraction a preventable behavior?
- Is Fat Injection Harmful?
- Is brain death reversible?
- Is alcohol good for the heart?
- Inflammation of the gallbladder What is cholecystitis?
- In Which Situations Is Breast Reduction Surgery Performed?
- In Which Part Of The Body Does The Polyp Appear?
- In Which Cases, Mammography Shots Are Started At An Earlier Age?
- In which cases is genital aesthetics performed?
- In a Family, The Heart is Very Vital.
- How to lower cholesterol
- How to feed in iron deficiency?
- How to Eat Before Sports?
- How to Deal with 2-Year-Old Syndrome?
- How to Be the Right Parent
- How should weight control be done?
- How Should We Feed During Seasons ?
- How Should We Eat While Receiving Chemotherapy?
- How should we eat to avoid winter diseases?
- How should it be fed during infancy?
- How Should Children Be Approached During Puberty?
- How should a regular diet be?
- How Often Should Lip Filling Be Renewed?
- How Often Should I Have A Mammogram?
- How Many Weeks Does a Twin Pregnancy Become Apparent?
- How Long Does Physical Therapy Take?
- How Long Does Breast Reduction Surgery Take?
- How Is the Recovery Process After Rhinoplasty Surgery?
- How is the jaw joint structure? What are jaw joint diseases?
- How is Male Breast Reduction Surgery Performed?
- How is incontinence treated?
- How is incontinence treated?
- How is Implant Bone Transplantation Performed?
- How is Breast Reduction Surgery Performed? Which Methods Are Used?
- How Does the Water in the Ear Come Out?
- How does the HPV virus show symptoms?
- HOW DOES FAMILY DISTURBING AFFECT CHILD DEVELOPMENT
- How does excess weight cause urinary incontinence?
- How can we protect ourselves from the flu?
- High blood pressure can cause these diseases.
- Harms of Glucose Syrup
- Hair Transplant Operation And After Process
- Hair Transplant Before and After
- Good News for the Little Hips !
- Golden Ratio Method
- For what diseases are antidepressants used?
- Follow the vaccination calendar for your child's health
- Factors Affecting Belly Fat:
- Expectant mothers should be informed about this.
- Effects of water on the body
- Effect of sunburn on babies
- Effect of salt use on kidneys
- Drinks for sore throat
- Don't Starve To Lose Weight Fast
- Don't forget to have your child's health check-ups before starting school.
- Does Vitamin D Deficiency Cause Depression?
- Does Having Moles Removed Cause Cancer ?
- Does cold weather affect lumbar hernia?
- Do Silicones Explode ?
- Do polyps of the large intestine turn into cancer
- Diseases caused by stress
- Differences Between FUE and DHI Hair Transplant
- Diagnosing Scoliosis in Children
- Dead inspection;
- Curious about heart rheumatism
- Celebrities' Choice of Spring Thread
- Causes of Insomnia
- Causes of Huntington's Disease
- Causes of Diarrhea
- Causes of Cracked Lips
- CAUSES OF BONE INFLAMMATION
- Care Recommendations For Dry Hair
- Can The Prosthesis Be Changed in Breast Augmentation?
- CAN SURGERY BE PERFORMED ON PREGNANT WOMEN?
- Can I Come From Abroad ?
- Can Diabetics Have Kidney Transplantation?
- Can Cardiovascular Patients fast ?
- Can Breastfeeding Women Have A Mammogram?
- Breast cancer treatment during pregnancy
- Breast cancer screening methods
- BONE INFLAMMATION (OSTEOMIELIT) TREATMENT
- Blood pressure can rise without a headache
- Before and After Maternity Aesthetics
- Are vitamin supplements necessary?
- 4 Ways to protect yourself from a southwest disease
- ?What Are FlaxSeeds Good For?
- ?What are Blueberries?
- What tests determine the source of impotence?
- What Is the Use of Hibiscus?
- What is Sedimentation?
- What Is Pollen Useful For?
- What is Phytotherapy?
- What is hand tremor?
- What Is Good for Acne Scars?
- What is Ginger?
- What is Entube ?
- What is cholesterol?
- What exercises are helpful in fibromyalgia?
- What Does Hawthorn Mean?
- What Does Amnesia Mean?
- What are the symptoms of anemia?
- What are Hemorrhoids (Hemorrhoids) Treatment Methods?
- The Benefits of Parsley Juice
- The Benefits of Eating Cherries
- The Benefits of Eating Bananas
- Tasks of the Limbic System
- Symptoms of a Stroke (Paralysis)
- Scoliosis Symptoms in Children
- Nutritional Recommendations for Liver Patients
- Liposuction (Vacuum Fat Extraction Surgery)
- Is There an Age Limit For Hair Transplant ?
- In Which Areas Is Blepharoplaty Applied?
- How to Do Meditation?
- How Many Calories in Dates?
- How Is Physical Therapy Done?
- How is it treated?
- Eye Diseases That Occur With Age?
- EFFECTS OF DRINKING WATER ON HEALTH:
- Can I Breastfeed After Breast Reduction Surgery?
- Blood Incompatibility Needle
- Basal Metabolic Rate
- Things to Know After Application Botulinum Toksin ?
- What is Pica Syndrome?
- What is Nigella?
Contact us
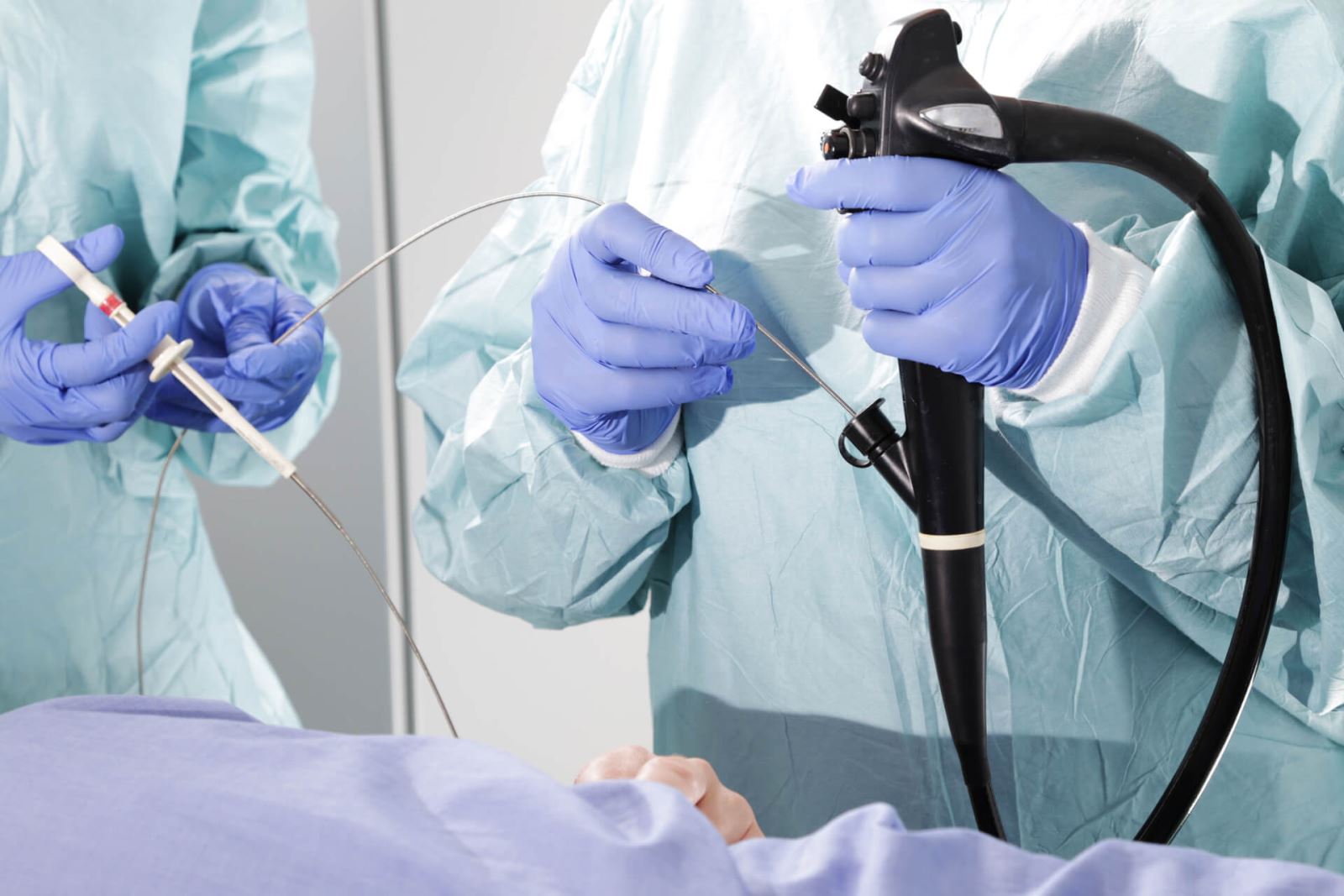 A small light and camera on the end called an endoscope, a device with the help of the esophagus,
A small light and camera on the end called an endoscope, a device with the help of the esophagus,